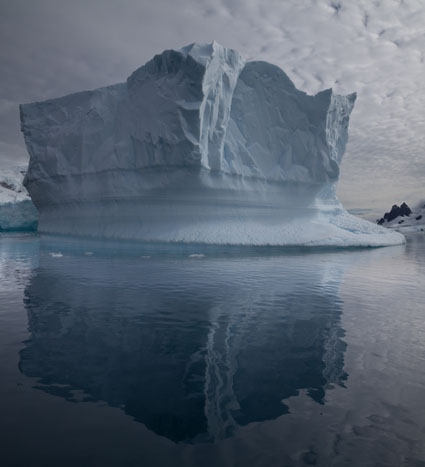
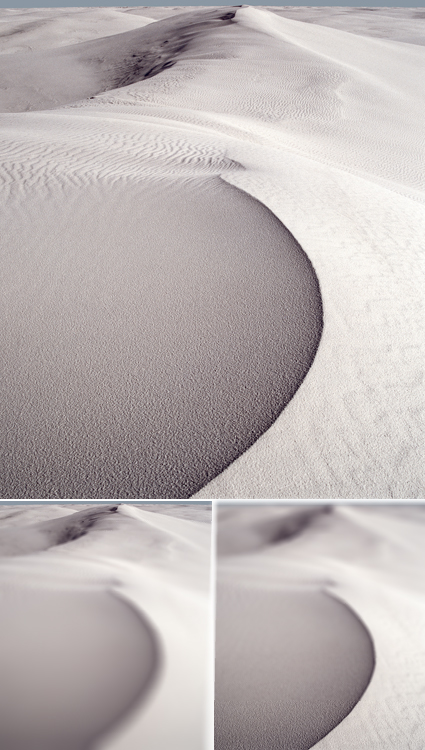
Controlling Blur FX With Photoshop
Photographers use blur (or bokeh) for a variety of reasons: to enhance space through depth of field; to add interesting visual artifacts; to simplify them; to change the quality of their expression. In the past, blur was controlled almost entirely through exposure; now it can also be controlled during post-processing, giving photographers an unprecedented array of options and ways to customize the look and feel of their images. Knowing what you can do, how far you can go, and when you can do it may change the way you shoot, one time, sometimes, or all the time.
There are many blur filters in Photoshop; Field Blur, Iris Blur, Tilt-Shift, Gaussian Blur, Lens Blur, Motion Blur, Radial Blur, Shape Blur, Smart Blur, Surface Blur (in order of appearance in the Filter: Blur drop down menu. The choices are extensive and it pays to familiarize yourself with your options by experimenting with them; you’ll find you have an extraordinary set of options that you can modify and combine creatively. If you only use the filters Gaussian Blur and Lens Blur, you’ll still have game-changing control at your fingertips, once you learn how to extend and modify them.
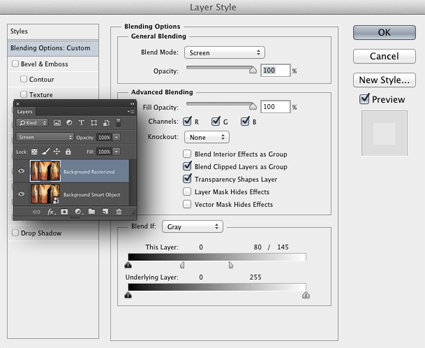
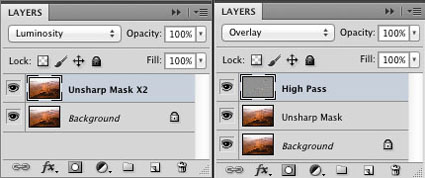
There are several important non-destructive strategies you can use to gain more control over all filter effects that will enable you to go further in your explorations and generate more sophisticated and compelling results Try one or all of the moves in this classic progression. Apply a filter to a duplicate layer and then modify its Opacity, Blend Mode, Blend If Sliders, and add a layer mask …
Read more on Digital Photo Pro.
Learn more in my digital photography and digital printing workshops.