Creative Image Sharpening With HDR Software
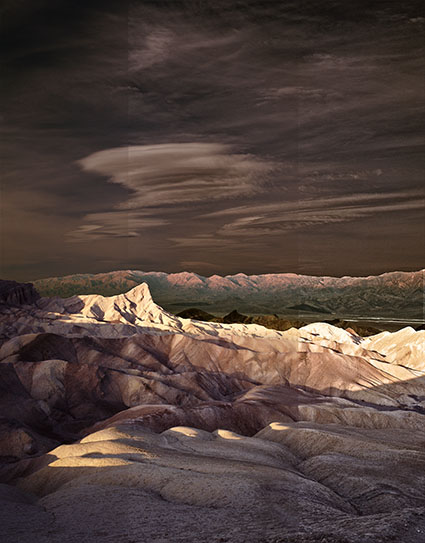
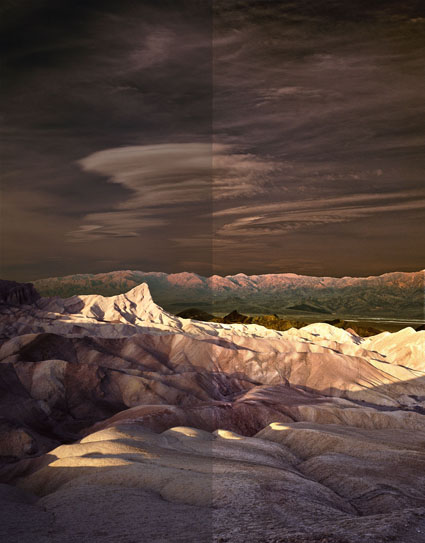
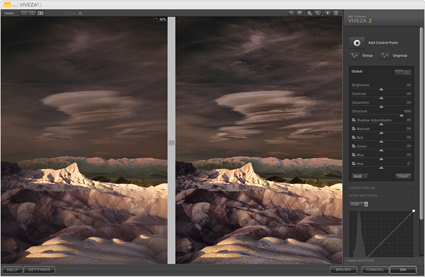
Unsharpened / Hybrid / Strong HDR
HDR software is most typically used to render shadow and highlight detail, but it can also be used to enhance tonal separation and detail in any range of tones, even in images with extremely low contrast. The very same tools that are used to compensate for HDR side effects can be used to sharpen any image.
When multiple bracketed exposures are merged into a single processed file, shadows and highlights that exceed the dynamic range of a camera’s sensor are compressed into the dynamic range of a digital file, taking the mid-tones with them. Depending on the HDR software used, a variety of tools are available to restore contrast and separation in mid-tones. If used aggressively, these tools produce the telltale signs of contemporary or grunge HDR artifacts – halos and texture accentuation. These are the very same artifacts that digital sharpening routines use more conservatively to make images appear sharper - only they look different.
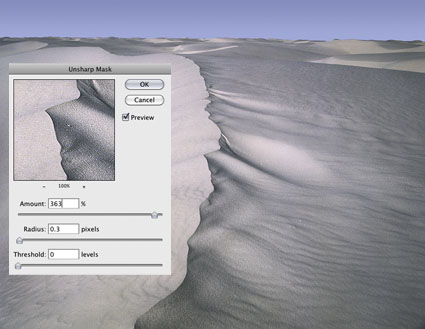
Unlike the hard halo and line produced by the filter Unsharp Mask and more like the soft line produced by the filter High Pass, HDR sliders can give you still more points of control over line and texture, each with a slightly different flavor.