The Easiest Way To Match Colors Exactly With Photoshop


Without Dehaze
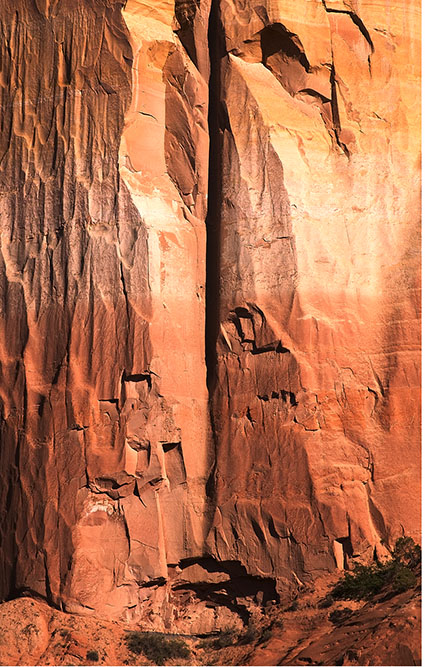
Dehaze may create color artifacts
Color artifacts removed
Color without Dehaze blended with luminosity with Dehaze
The top layer is set to a blend mode of Color
When you’re using Lightroom or Camera Raw, you’ll quickly find the Dehaze slider can produce marvelous contrast effects. Dehaze can dramatically exceed the contrast that can be produced with either Curves or Clarity. Sometimes it will reveal detail you couldn’t see with your eyes!
.
Often, there’s a price to pay for these great effects – color shifts. Neutral areas may turn magenta. Shadows may pick up strong blue or green casts. To make matters worse, these unwanted artifacts are rarely uniform, which makes them harder to fix.
.
If you’re lucky you can compensate by reducing Saturation after using Dehaze. When you do this, it’s likely that you’ll end up choosing the least objectionable version or making a compromise you’d prefer not to. Frequently, to avoid these side effects, you’ll be tempted to not to push Dehaze as far as you’d like to.
There is a cure that will help you go as far as you’d like, without producing color shifts. Render your image twice. First, render it with as much Dehaze as you’d like. Second, render it without Dehaze.
.
Then place the version without Dehaze in a layer on top of the version with Dehaze. Change the Blend Mode of the top layer to Color. This will give you a combination of the color of the top layer (without Dehaze’s color artifacts) and the luminosity of the bottom layer (with Dehaze’s contrast).
.
How do you make two layers from one Raw file?
.
If you’re using Lightroom, make a virtual copy and then double click on the Dehaze slider. Highlight the original file and the virtual copy and select Photo > Edit In > Open as Layers in Photoshop. Now in Photoshop, make sure to change the top layer’s blend mode from Normal to Color.
.
If you’re using Camera Raw, open your Raw file as a smart object, then select New Smart Object via Copy in the Layer menu, and finally double click on the top layer to return the Dehaze slider to 0. Remember, change the top layer’s blend mode from Normal to Color.
.
The technique of using the color of one layer to overlay another layer can be used for many applications. Here, it makes Dehaze even more useful.
.
Read more color adjustment resources here.
Learn more in my digital photography and digital printing workshops.
Before sharpening
Unsharp Mask only
Unsharp Mask and High Pass filters combined
Different sharpening techniques make the world look different. A world of difference can be seen between the thin hard line of Unsharp Mask and the broad feathered line of High Pass Sharpening.
Can you choose a combination of both? Yes, you can! You can choose the texture of one, the halo of another, and the line of yet another, applying them either globally or selectively. You can customize the look and feel of detail in any image or image area with astonishing precision and flexibility.

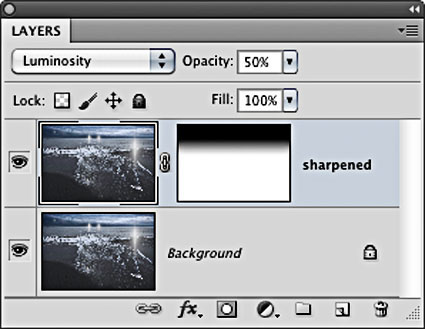
Layers have Blend Modes and can be masked
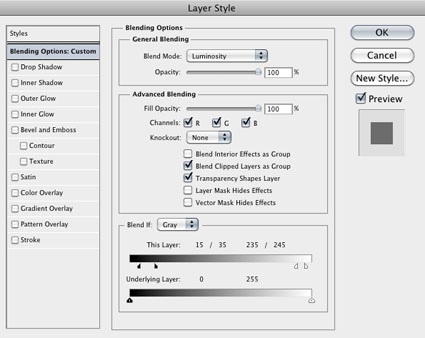
Double click a layer to activate its Blend If sliders
There are many reasons to use layers when sharpening your digital images.
How do you do this? Simply duplicate the Background layer and sharpen the new layer.
Eliminate Saturation Shifts
Layers can be used to eliminate saturation shifts. Change the Blend Mode of a sharpening layer from Normal to Luminosity. Color noise will also be reduced this way.
Before channel blending
After channel blending
Big problems call for big solutions. Blending channels is a powerful color adjustment strategy that can handle even the biggest challenges.
Color adjustment occurs by modifying the tonal structure of individual grayscale channels. Typically, the information within them is adjusted. Less typically, the information within them is replaced.
Blending channels is one way of replacing them. Blending channels takes information from one channel and combines it with information from another. Rather than simply enhancing existing tonal values, blending channels reshapes one channel’s tonal structure with another’s. Consequently, in a most cases, blending channels calls for a substitution of information by percentage not a wholesale replacement of the deficient channel. You usually blend channels from different versions of the same image because blending channels from different compositions produces a highly altered effect.
Blending channels is complex. It often produces additional unintended color affects that may require further correction, such as shifts in hue that aren’t uniform across the tonal scale. Blending channels is neither the simplest nor the most direct path to color adjustment, but in certain situations (files that are exceptionally problematic) it may be the best path. The resulting benefits can be dramatic.
When is blending channels appropriate? In extreme cases. Blending channels is designed to correct major color deficiencies. It’s recommended if a channel is severely deficient, either globally or in select areas. For example, by being extremely light or dark or having very low contrast, a channel may be lacking desired detail. That detail can be found in another channel. Fine-tuning color is best left to more traditional methods of color adjustment.
Many Methods
There are several ways to blend channels; Channel Mixer, Apply Image, Calculations, and using channels as layers. Let’s review the options in detail.
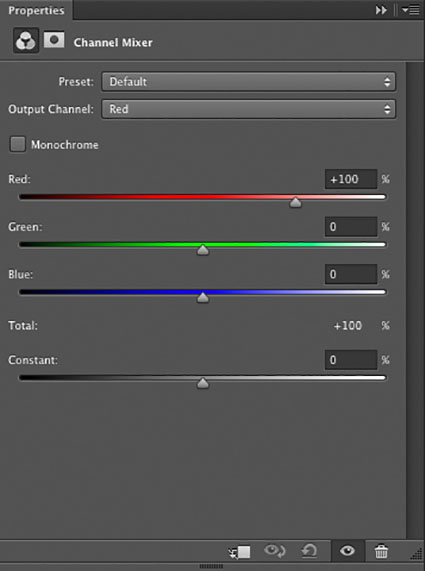
The Channel Mixer (Layer: New Adjustment Layer: Channel Mixer) blends percentages of channels within a single document. It can be applied as an adjustment layer and so corrections made this way can be changed or masked indefinitely. It cannot be used to blend channels from two documents. The Channel Mixer is an excellent choice for making global (the same percentage of channels for the whole image) color to black-and-white conversions. If you want to control black-and-white conversions locally (different percentages of channels for different image areas), use channels as layers instead.
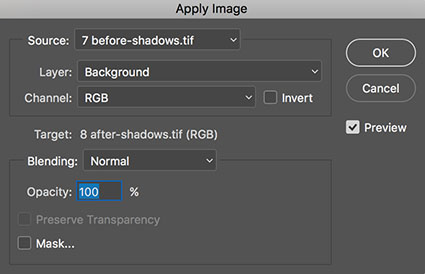
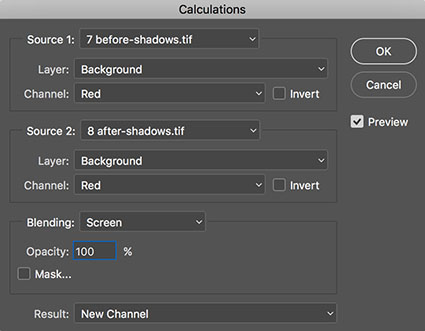
The commands Calculations (Image: Calculations) and Apply Image (Image: Apply Image) can also be used to blend channels. With these two commands you can combine any two channels, from different documents, from any layer, at any opacity, with most blend modes. With Apply Image you target the channel you wish to change. With Calculations you blend to create a new document, a new channel, or a new selection. Neither Calculations nor Apply Image can be used as adjustment layers or layers, consequently corrections you make with either of these features are made permanently to an image. With Apply Image and Calculations you can take advantage of two less frequently used blending modes not found with other tools (Add and Subtract) but you cannot take advantage of four frequently used blending modes (Hue, Saturation, Color, and Luminosity) – even if you use the Fade command.
For the greatest control and flexibility use channels as layers. How do you do this? Copy any channel and paste it into any destination as a layer. (Target a channel (click on it); copy it (Select: All; Edit: Copy); then target the master channel (RGB) and paste (Edit: Paste).) You can activate, deactivate, mask, change, or replace this new layer indefinitely. Use Layer Styles (double click on the layer icon in the Layers palette) to determine Blend Mode, Opacity, Advanced Blending (to select which channel is affected) and Blend If options (to determine how This Layer affects the Underlying Layer or which values of the overlying layer affect the values of the underlying layer). What’s more, you get a dynamic preview of any changes you make while you make them. The adjustments you make are flexible, so you can remove them or fine-tune any of the settings future editing sessions. You can even blend two or more channels first, as layers, and then use the resulting new layer to blend with the Background layer. By turning channels into layers, you can achieve everything that the other methods achieve and more.
One File, Many Channels
You may be surprised to find that every file has at least ten channels to choose from. How do you get so many? Consider the file in different color spaces – RGB, CMYK, and LAB. Convert a duplicate file into another color space and you can use any and all of the resulting channels. In fact, you can choose between many, many more channels when you consider that when converting to CMYK there are five different options for generating a Black Plate (None, Light, Medium, Heavy, and Maximum) with two styles for each with two Separation Types (UCR and GCR). But, for the vast majority of situations, I recommend you try to keep things as simple as possible and stick with the standard three.
Be cautious with older files and lower end scanners when blending with the blue channel as it often contains significant amounts of noise. In fact, in some instances, blending channels can be used to replace some or all of the blue channel and thereby remove unwanted noise. Unlike blurring or despeckling, this method of removing noise will not compromise sharpness, but it may produce unwanted color shifts that will require subsequent correction.
A Good Preview
The possibilities are staggering. Is there anything that can help with the decision making process? Yes. A good preview. You’ll want to have multiple documents of the same image in different color modes (RGB, CMYK, LAB) visible at one time to simultaneously see the blended and the blendee. You may even want to make a side-by-side comparison of the component channels of a single document. To do this, use the Split Channels option in the Channels palette submenu. This command will break a single multi-channel document into multiple single-channel documents. (If a file has layers it must be flattened first to use Split Channels.) While doing this with several documents will quickly fill a screen, having the channels separated makes evaluating their relative merits infinitely easier.
Classic Strategies
With so many possibilities, how do you choose one channel as the best candidate to blend with another and how do you use it?
First, identify the channel causing the problem. Then, find the channel with the best contrast in the areas you wish to enhance (at a low opacity) or replace (at 100% opacity). (Stronger adjustments require higher opacities.) Finally, deal with any unintended side effects.
There are several tried and true strategies for dealing with classic problems. First, create detail where there was none before. Second, create contrast that wasn’t there before. Third, add more contrast to existing tonal relationships, if the values can’t be adequately enhanced using Curves.
Look to the Luminosity channel in LAB. Look to the black plate in CMYK. Look to complementary colors. Complementary colors often contain the best possibilities for increasing contrast (Red and Cyan, Green and Magenta, Yellow and Blue), in highly saturated values.
What are you looking for? Better detail in shadows or highlights, better contrast, and a similar tonal distribution. If you change the relative distribution of tones in a channel, you’ll create a non-uniform color shift where some colors will shift more dramatically than others.

Sometimes channel blending produces unintended side effects.
In most cases, these side effects can be cured.
Blending channels can produce unintended side effects. There are times when it’s better to achieve the necessary effect with this technique and accept its side effects, if the side effects are easier to cure than the initial problem. Typically, all that’s required is a little dose of additional tonal enhancement, either to the master channel (tone and contrast) or a single channel (color). If you find this is not the case, take this as a sign that this is not the right technique for the problem you face.
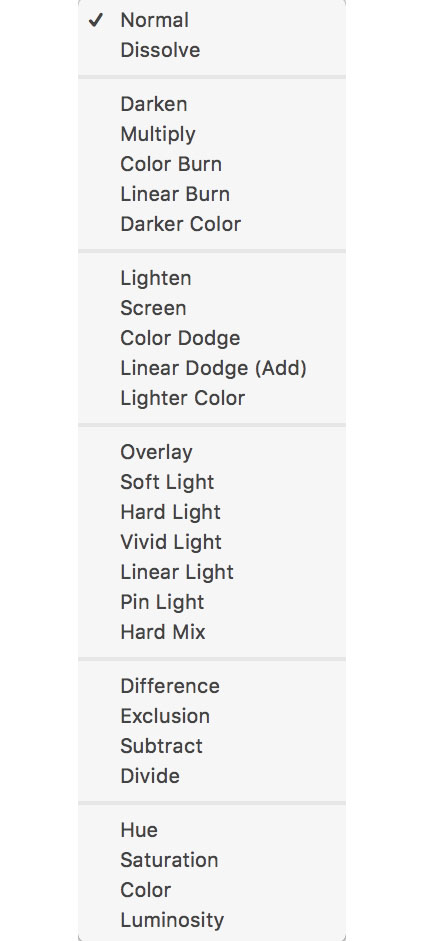
Layers offer many Blend Modes
Control The Mix With Blend Modes
As well as controlling the amount channels are blended you can control the way they are blended, by using blending modes. Blend modes determine how new values are mixed with old values. There are dozens of blend modes to choose from.
As color adjustment is achieved by altering the luminance (light and dark) values of select channels (Channels create but don’t contain color or saturation.), when it comes to blending channels, you can limit the number of blend modes you use to those that affect tone; five are particularly useful – Lighten, Screen, Darken, Multiply, and Luminosity.
Lighten displays the lightest values of both This Layer and the Underlying Layer; its neutral color is black (you can’t lighten with black).
Screen multiplies the inverse values of the pixels lightness or darkness. It’s like registering same image in the same location from two projectors. Think of it as industrial strength lightening. Its neutral color is black (you can’t lighten with black). Screen can do wonders for opening up deep shadows. It has a tendency to blow out highlights. Use a contrast mask to remove the effect from highlights.
Darken displays the darkest values of both This Layer and the Underlying Layer; its neutral color is white (you can’t darken with white).
Multiply multiplies the values of the pixels on both layers and then divides by 255. It’s like registering two identical transparencies on a light table. Think of it as industrial strength darkening. Its neutral color is white (you can’t darken with white). Multiply can do wonders for reclaiming subtle highlight detail. It has a tendency to block up shadows. Use a contrast mask to remove the effect from shadows.
Luminosity combines the luminance values of This Layer with the hue and saturation of the Underlying Layer; it has no neutral color.
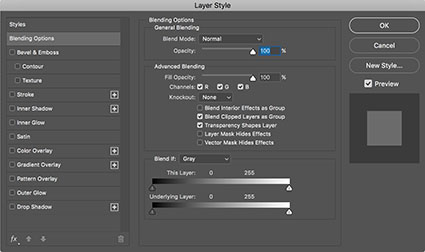
Enhance The Blend
You can enhance a channel before (or if you use channels as layers after) blending it with another. Use any adjustment method that makes the data better to blend with. As you’re blending with black-and-white images, Curves is usually all you need for it offers the most precise control of tone. For instance, you might increase the contrast of an image before using it to blend with. If you’re using the channels as layers method, all you have to do is group a Curves adjustment layer to the new layer being used to blend with. The contrast of overlying layer can then be fine-tuned as the blend with the underlying layer is occurring. This way you don’t have to guess how much contrast needs to be added before blending, instead you see how much contrast to add while the blend is occurring.
Constraining The Effect
While blending channels may solve problems that other adjustment methods can’t, they may also produce new problems.
In a great many cases, if the tonal distribution of a single channel is substantially altered using another channel, color may shift in an unintended manner. If this happens simply make an additional adjustment to eliminate any side effects. There are times when the color shifts you encounter will be non-uniform (more in some areas than others), which may lead you to making more complex corrections than you had anticipated.
If the problem solved with channel blending and the resulting side effects lie in different areas of the image, consider masking away the side effects rather than correcting them. There are several ways of masking the side effects of channel blending from selected areas. One, simply brush them away by painting with a black brush on a layer mask. Two, use a contrast mask to hold back the effect from highlights or shadows. Three, use the Blend If function in Layer Styles; by sliding the black arrow to the right or the white arrow to the left you drop out the effects from values below or above them – by holding the Option key (Command on PC) you can split the sliders to fade the effect more smoothly.
If you think you’re not used to blending channels, think again. Every time you turn a color image into a black-and-white image you blend channels. In a grayscale conversion three channels are blended to create a single channel while when using either Hue/Saturation or Channel Mixer three channels are blended to equal RGB values. But, when it comes to color adjustment, blending channels is used infrequently, perhaps because it’s so little known. Blending channels is a sophisticated adjustment method. In a majority of cases you don’t need a method that’s this complex. Blending channels is best used in exceptional situations for enhancing originals with substantial problems. If you find that you use this technique frequently, you’re probably not addressing the real problem, the quality of your originals. Nevertheless, when you run into files with severe problems, blending channels will often save the day.
Read more on Color Adjustment here.
Learn more in my digital printing and digital photography workshops.

There are many things you can do in Photoshop to make the most of shadow and highlight detail in images, even if you didn’t bracket exposures for HDR.
Curves
Curves, the most precise tool for modifying brightness and contrast, allows you to target and adjust shadows and highlights independently of one another. You can use it to reduce contrast and render more detail in very bright highlights and/or very dark shadows. The Curves interface has a feature (The icon looks like a finger with up and down arrows.) that allows you to click on any area of an image to place a point and adjust those values. If you’re adjusting highlights and shadows, it’s quite likely that you will also have to adjust values in the other end of the tonal scale and possibly midtones to generate the best results. Keep it simple; it’s surprising what you can do with just two or three points. Keep it smooth; avoid posterization by not flattening areas of a curve. The Blend Mode Luminosity can be used to remove any unintended shifts in saturation; more contrasti increases saturation while less contrast decreases saturation.
Curves can be used to lighten shadows and/or darken highlights

Before Curves

After Curves

Contrast added – Normal and Luminosity blend modes compared.
Hue adjusted – Normal and Hue blend modes compared.
Hue adjusted – Normal and Color blend modes compared.
Saturation added – Normal and Saturation blend modes compared.
When you adjust color in digital images, several common unintended byproducts arise. Increase or decrease contrast and saturation will rise or fall. Increase or decrease saturation and lightness will change. Make a hue adjustment with Curves (or Levels) by targeting specific channels, and an image will either lighten or darken. Make a hue adjustment with Hue/Saturation, and both saturation and luminosity are likely to shift, sometimes lightening and other times darkening. Correct one problem, and you may create another. Sometimes these byproducts are desirable; usually, they are not. While these changes may be minor, sometimes insignificant, when making subtle adjustments, they can become major when making more dramatic adjustments.
Is there a cure? There are several!
You can make additional adjustments to correct the byproducts of one adjustment. For instance, to compensate for value shifts when making color adjustments by targeting individual channels with Levels or Curves, many return to the Master channel to correct the accompanying shifts in value. To correct saturation shifts when contrast has been increased or decreased, a second adjustment is often made with Hue/Saturation. Some of these moves bring new problems with them, which will, in turn, need additional adjustment. If the problems are minor, usually, the byproducts are accepted. This is appropriate only when the byproducts are desirable and far less than ideal when they are not.
Most of these moves are made in an attempt to stabilize one component of color while another shifts.
Color can be broken down into three essential elements; hue (a spectrum around the color wheel from red through yellow, green, blue, cyan, magenta, and back to red), saturation (a gradient from intense to dull), and luminosity (a gradient from dark to light). These problematic byproducts, typically found in standard methods of color adjustment, arise because only a few exotic color spaces treat the three distinct qualities of color separately. To control only one quality in RGB and CMYK, you typically have to make adjustments to more than one channel. In LAB, luminosity has its own separate channel, and you can make adjustments to it alone, but saturation and hue are still wrapped into two channels, A and B. The color spaces that treat all three elements separately, HSB, HSL, and HSV, are not supported by Photoshop (or Lightroom).
Some adjustment tools allow you to make adjustments to one component of color without affecting the others. Favor them whenever practical. For instance, you can check Preserve Luminosity when using Color Balance to stabilize brightness when making adjustments to hue. This works well when adjustments are made to the midtones. But, when targeting highlights and/or shadows, brightness or contrast may shift. Tools like these build the solution for the problem directly into their interface. But these tools are not always the tools we need to accomplish a given task, nor are they the most precise.
Some tools even produce problems that are not curable. For example, increasing or decreasing value using the Lightness slider with Hue/Saturation will reduce an image’s dynamic range, making white or black gray while darkening or lightening. The best policy is to avoid using these tools altogether. You can do more and do it with greater precision using other tools. (In this specific case, use Curves.)
Wouldn’t it be nice if you could target one specific component of color without affecting the others with any color adjustment tool? When you use Photoshop, you can. You can use the blending mode of adjustment layers to constrain the effects of an adjustment to one or more components of a color. If you are making an adjustment directly to an image without using adjustment layers, you can Fade (Edit: Fade) the problem away immediately after applying the adjustment. Unfortunately, you cannot do this during Raw conversion with either Lightroom or ACR. Many of these side effects are built into the behavior of the sliders, and no additional blend mode feature exists.
You’ll find all of the blend modes in Photoshop’s Layers palette. All layers, including adjustment layers, have a blending mode. A layer can only have one blending mode, but a layer’s blending mode may be changed at any time. The default is Normal. But there are many other modes to choose from. The long list of options you will find under the blending mode pull-down menu, offering seventeen choices in all, may seem overwhelming at first and deter you from using them altogether. While some experimentation with all of the blending modes may prove fruitful, start with the four that are most useful for color adjustment – the four that target specific components of color; Hue, Saturation, Color, and Luminosity.
You can use the adjustment layer blending modes of Hue, Saturation, Color, and Luminosity, to target single color components, regardless of which space you are editing in. The blending mode of an adjustment layer constrains the effects of an adjustment to the component of the color specified in its title. Hue allows an adjustment layer to affect only hue, eliminating shifts in luminosity. Saturation allows an adjustment layer to affect only saturation, eliminating shifts in luminosity. (Use this for most saturation adjustments, for instance, when you use Hue/Saturation.) Color allows an adjustment layer to affect both hue and saturation, eliminating shifts in luminosity. (Use this for most hue adjustments, for instance, when you use a single channel in Curves.) Luminosity allows an adjustment layer to affect only value or brightness, eliminating shifts in saturation. (Use this for most contrast adjustments, for instance, when you use the master channel in Curves. This functions just like adjusting the L channel in LAB without having to make a color mode conversion, possibly forcing you to flatten a file.)
You can specify the blending mode of an adjustment layer when you first create it. Or, you can change the blending mode of an adjustment layer after its creation. Either way, it’s more than likely that you will want to compare the effects of both the alternate blending mode and the Normal blending mode. Sometimes, you may find you like the side effects and don’t want to remove them. In these cases, leave the blend mode on its default Normal. As a rule, with exceptions, I recommend you use the blend mode that targets the element of color you are adjusting.
You cannot reduce a blending mode by a percentage; it’s an all-or-nothing proposition. If, for instance, you want to remove most, but not all, of the additional saturation introduced by a shift, in contrast, you will need to choose a blending mode, either blending mode – Normal or Luminosity and then make an additional Hue/Saturation adjustment. Pick the mode that gets you closest to the result you desire, and then fine-tune the final effect with a subsequent adjustment.
The precision and degree of control over color you can acquire today is nothing short of astonishing. It is responsible for producing a dramatic r/evolution in color photography. We now have near total control of color’s three primary elements – hue, saturation, and luminosity. Add to this nonlinear color adjustment (even color transformation) the ability to affect specific hues without affecting others. Add to this the ability to make adjustments to specific ranges within each of those components, for instance, the saturation of highlights and/or shadows, rather than the component in its entirety. And there are many other possibilities. You can do virtually anything. You need only imagine the possibilities and then find the right tool for the job.
Read more about Color Adjustment here.
Learn more in my digital photography and digital printing workshops.

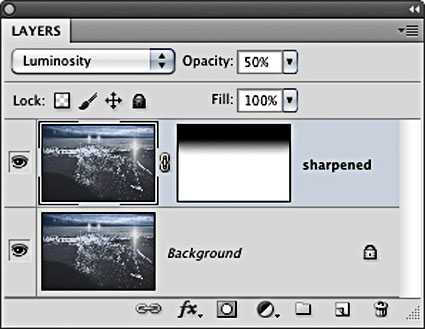
There are many reasons to use layers when sharpening your digital images.
Layers can be used to eliminate saturation shifts. Change the Blend Mode of a sharpening layer from Normal to Luminosity. Color noise will be reduced this way.
Deke McClelland shows you how to use stacks to remove moving objects in a scene.
This is a game changing technique I emphasize in all of my field workshops.
It will open up new possibilities for you, change the way you shoot, and raise your success rate.
Learn more from Deke McClelland here.
Read more in my digital photography and digital printing ebooks.
Learn more in my digital photography and digital printing workshops.